Data Generation in AI through Transport and Denoising – EchoCem Challenge
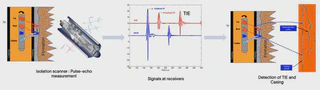 EchoCem Challenge: Isolation scanner pulse-echo measurement process for detecting TIE (Third Interface Echo) and casing in ultrasonic well imagery segmentation.
EchoCem Challenge: Isolation scanner pulse-echo measurement process for detecting TIE (Third Interface Echo) and casing in ultrasonic well imagery segmentation.This project was performed under the “Data Generation in AI by Transport and Denoising” course led by Stéphane Mallat (Collège de France), as part of the Master MVA curriculum.
We took part in the EchoCem Data Challenge, focused on segmenting ultrasonic well images to estimate casing and the Third Interface Echo (TIE) in noisy measurement environments.
Our model was ranked 1st on both public and private leaderboards among all participating teams.
Objective
Design a segmentation model robust to sensor noise and structural variability, to identify the casing and TIE interfaces in geophysical ultrasonic data.
Methodology
Baseline & Handcrafted Models
- Explored Random Forest classifiers using texture filters, Sobel / gradient features, local statistics
- Reviewed limitations in generalization and adaptation to unseen wells
Deep Segmentation Approach
- Adopted U-Net with a ResNet34 encoder, pretrained, fine-tuned for the dataset
- Employed Focal Dice Loss to address strong class imbalance
- Extensively used data augmentations (rotations, affine transforms, noise corruption)
Post-Processing Refinement
- Morphological filtering to smooth boundaries
- Secondary U-Net to refine soft predictions into crisp segmentation masks
Results
| Metric | Public Leaderboard | Private Leaderboard | Baseline Benchmark |
|---|---|---|---|
| IoU (mean) | 0.6821 | 0.6818 | 0.4086 |
Our model achieved top rank in both evaluations, demonstrating excellent generalization and robustness to noisy imaging conditions.
Key strengths included stable training, effective augmentation, and hybrid correction networks.
Technical Observations
- Focal Dice Loss was crucial for training stability under class imbalance
- The U-Net + ResNet34 backbone captured both fine edges and contextual information
- The refinement U-Net consistently improved segmentation quality
- Ablation studies showed diminishing returns beyond moderate resolution (~160×160)
Key Takeaways
- Deep segmentation models can extract meaningful structure from noisy geophysical imagery
- Hybrid strategies (classical + learned) enhance robustness and interpretability
- The transport / denoising perspective helps bridge physical models and learned architectures
- The project may generalize to other modalities, e.g. medical ultrasound or non-destructive testing
References
- Mallat, S. (2024). Génération de données en IA par transport et débruitage. Collège de France
- Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T. (2015). U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation
- He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J. (2015). Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition